|
trace工具以及排序优化(order by 以及文件排序filesort)
每天多学一点点~ 话不多说,这就开始吧…
文章目录
trace工具以及排序优化(order by 以及文件排序filesort)1.前文2.准备工作3.mysql如何选择索引4.trace工具用法5.常见sql排序优化6.Using filesort文件排序7.结语
1.前文
承接上文 mysql优化——2.explain详解与实践 ,有时候遇到一些sql,用explain执行计划分析的时候与你想的不一样,明明根据底层B+Tree应该会走索引,可是偏偏没走,今天博主就来研究研究下mysql的另一个分析工具,trace工具 博主用的版本是mysql5.7.24,不同版本会稍有不同 (博主之前一直用的是maradb10.2.14,没有trace工具,直到10.4.3版本才引入)
2.准备工作
执行下列sql
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `employees`;
CREATE TABLE `employees` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(24) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '姓名',
`age` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '年龄',
`position` varchar(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '职位',
`hire_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT current_timestamp() COMMENT '入职时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `idx_name_age_position` (`name`,`age`,`position`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=7 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='员工记录表';
3.mysql如何选择索引
我们先来看下下面几个例子
EXPLAIN select * from employees where name > ‘a’; 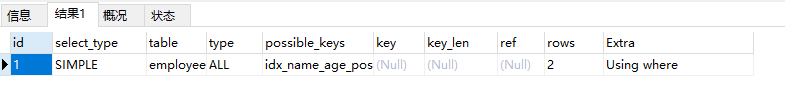 这里没有走索引,分析如下: 如果用name索引需要遍历name字段联合索引树,然后还需要根据遍历出来的主键值去主键索引树里再去查出最终数据,成本比全表扫描 还高。(name是非主键索引,也称辅助索引,其叶子节点存储的是主键id。所以会查两次) 可以用覆盖索引优化,这样只需要遍历name字段的联合索引树就能拿到所有结果(因以为要查询的数据都在联合索引里面,所以只要查一次索引树,成本会比全表扫描还高),如下: 这里没有走索引,分析如下: 如果用name索引需要遍历name字段联合索引树,然后还需要根据遍历出来的主键值去主键索引树里再去查出最终数据,成本比全表扫描 还高。(name是非主键索引,也称辅助索引,其叶子节点存储的是主键id。所以会查两次) 可以用覆盖索引优化,这样只需要遍历name字段的联合索引树就能拿到所有结果(因以为要查询的数据都在联合索引里面,所以只要查一次索引树,成本会比全表扫描还高),如下:
EXPLAIN select name,age,position from employees where name > ‘a’ ; 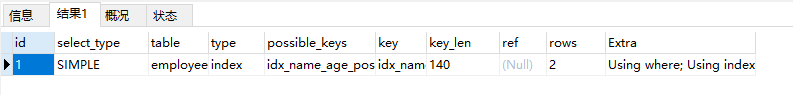 那么,神奇的地方来了,我们再来看看这条sql 那么,神奇的地方来了,我们再来看看这条sql
EXPLAIN select * from employees where name > ‘z’ ; 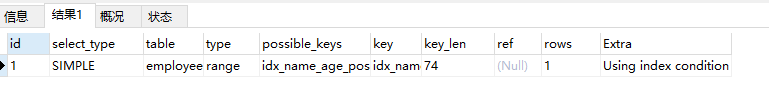 可能有小伙伴就会蒙蔽了,为何这句就走索引了,这和刚才 name > ‘a’ 不是差不么? 分析: 可能有小伙伴就会蒙蔽了,为何这句就走索引了,这和刚才 name > ‘a’ 不是差不么? 分析:
因为name字段里面的数据没有z开头的,用’z’查询的数据几乎没有或者很少,所以走辅助索引效率会更快。但是具体的,mysql最终是否选择走索引或者一张表涉及多个索引,mysql最终如何选择索引,我们可以用trace工具来一查究竟,开启trace工具会影响mysql性能,所以只能临时分析sql使用,用完之后立即关闭
4.trace工具用法
1 set session optimizer_trace="enabled=on",end_markers_in_json=on; ‐‐开启trace
2 mysql> select * from employees where name > 'a' order by position;
3 mysql> SELECT * FROM information_schema.OPTIMIZER_TRACE;
4 set session optimizer_trace="enabled=off"; ‐‐关闭trace
我们首先执行1,然后选中2 3 一起执行,分析完后记得执行4,用完之后立即关闭 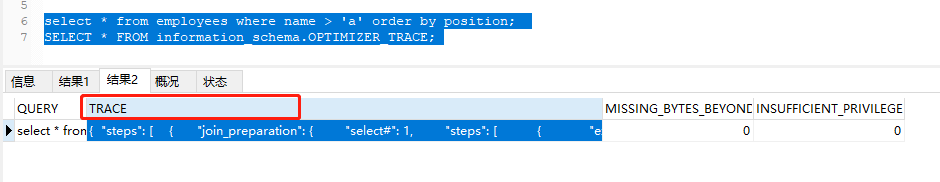 因为是以json格式输出的,将这一栏数据copy出来,去json转换的网站格式化看一下,请认真看下博主加注释的地方,如下: 因为是以json格式输出的,将这一栏数据copy出来,去json转换的网站格式化看一下,请认真看下博主加注释的地方,如下:
{
"steps": [
{
"join_preparation": { ‐‐第一阶段:SQL准备阶段
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
{
"expanded_query": "/* select#1 */ select `employees`.`id` AS `id`,`employees`.`name` AS `name`,`employees`.`age` AS `age`,`employees`.`position` AS `position`,`employees`.`hire_time` AS `hire_time` from `employees` where (`employees`.`name` > 'a') order by `employees`.`position`"
}
] /* steps */
} /* join_preparation */
},
{
"join_optimization": { ‐‐第二阶段:SQL优化阶段
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
{
"condition_processing": { ‐‐条件处理
"condition": "WHERE",
"original_condition": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')",
"steps": [
{
"transformation": "equality_propagation",
"resulting_condition": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')"
},
{
"transformation": "constant_propagation",
"resulting_condition": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')"
},
{
"transformation": "trivial_condition_removal",
"resulting_condition": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')"
}
] /* steps */
} /* condition_processing */
},
{
"table_dependencies": [ ‐‐表依赖详情
{
"table": "`employees`",
"row_may_be_null": false,
"map_bit": 0,
"depends_on_map_bits": [
] /* depends_on_map_bits */
}
] /* table_dependencies */
},
{
"ref_optimizer_key_uses": [
] /* ref_optimizer_key_uses */
},
{
"rows_estimation": [ ‐‐预估表的访问成本
{
"table": "`employees`",
"range_analysis": {
"table_scan": { ‐‐全表扫描
"rows": 3, ‐‐扫描行数
"cost": 3.7 ‐‐查询成本
} /* table_scan */,
"potential_range_indexes": [ ‐‐查询可能使用的索引
{
"index": "PRIMARY", ‐‐主键索引
"usable": false,
"cause": "not_applicable"
},
{
"index": "idx_name_age_position", ‐‐辅助索引
"usable": true,
"key_parts": [
"name",
"age",
"position",
"id"
] /* key_parts */
}
] /* potential_range_indices */,
"setup_range_conditions": [
] /* setup_range_conditions */,
"group_index_range": {
"chosen": false,
"cause": "not_group_by_or_distinct"
} /* group_index_range */,
"analyzing_range_alternatives": { ‐‐分析各个索引使用成本 很重要!!!!
"range_scan_alternatives": [
{
"index": "idx_name_age_position",
"ranges": [
"a < name" --索引使用范围
] /* ranges */,
"index_dives_for_eq_ranges": true,
"rowid_ordered": false, ‐‐使用该索引获取的记录是否按照主键排序
"using_mrr": false,
"index_only": false, ‐‐是否使用覆盖索引
"rows": 3, ‐‐索引扫描行数
"cost": 4.61, ‐‐索引使用成本
"chosen": false, ‐‐是否选择该索引
"cause": "cost"
}
] /* range_scan_alternatives */,
"analyzing_roworder_intersect": {
"usable": false,
"cause": "too_few_roworder_scans"
} /* analyzing_roworder_intersect */
} /* analyzing_range_alternatives */
} /* range_analysis */
}
] /* rows_estimation */
},
{
"considered_execution_plans": [
{
"plan_prefix": [
] /* plan_prefix */,
"table": "`employees`",
"best_access_path": { ‐‐最优访问路径
"considered_access_paths": [ ‐‐最终选择的访问路径
{
"access_type": "scan", ‐‐访问类型:为scan,全表扫描
"rows": 3,
"cost": 1.6, ‐‐确定选择
"chosen": true,
"use_tmp_table": true
}
] /* considered_access_paths */
} /* best_access_path */,
"cost_for_plan": 1.6,
"rows_for_plan": 3,
"sort_cost": 3,
"new_cost_for_plan": 4.6,
"chosen": true
}
] /* considered_execution_plans */
},
{
"attaching_conditions_to_tables": {
"original_condition": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')",
"attached_conditions_computation": [
] /* attached_conditions_computation */,
"attached_conditions_summary": [
{
"table": "`employees`",
"attached": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')"
}
] /* attached_conditions_summary */
} /* attaching_conditions_to_tables */
},
{
"clause_processing": {
"clause": "ORDER BY",
"original_clause": "`employees`.`position`",
"items": [
{
"item": "`employees`.`position`"
}
] /* items */,
"resulting_clause_is_simple": true,
"resulting_clause": "`employees`.`position`"
} /* clause_processing */
},
{
"refine_plan": [
{
"table": "`employees`",
"access_type": "table_scan"
}
] /* refine_plan */
},
{
"reconsidering_access_paths_for_index_ordering": {
"clause": "ORDER BY",
"index_order_summary": {
"table": "`employees`",
"index_provides_order": false,
"order_direction": "undefined",
"index": "unknown",
"plan_changed": false
} /* index_order_summary */
} /* reconsidering_access_paths_for_index_ordering */
}
] /* steps */
} /* join_optimization */
},
{
"join_execution": { ‐‐第三阶段:SQL执行阶段
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
{
"filesort_information": [
{
"direction": "asc",
"table": "`employees`",
"field": "position"
}
] /* filesort_information */,
"filesort_priority_queue_optimization": {
"usable": false,
"cause": "not applicable (no LIMIT)"
} /* filesort_priority_queue_optimization */,
"filesort_execution": [
] /* filesort_execution */,
"filesort_summary": {
"rows": 3,
"examined_rows": 3,
"number_of_tmp_files": 0,
"sort_buffer_size": 200704,
"sort_mode": ""
} /* filesort_summary */
}
] /* steps */
} /* join_execution */
}
] /* steps */
}
结论:rows_estimation(预估表的访问成本)中查询成本为低于analyzing_range_alternatives(分析各个索引使用成本)的查询成本,所以mysql最终选择索引扫描
5.常见sql排序优化
为了引入文件排序,咱们先来看看一下几种sql优化
Order by与Group by优化
EXPLAIN select * from employees where name=‘baoliewuqiu’ and position=‘dev’ ORDER BY age  利用最左前缀法则:中间字段不能断,因此查询用到了name索引,从key_len=74也能看出,age索引列用 在排序过程中(name已经是常量了),因为Extra字段里没有using filesort 利用最左前缀法则:中间字段不能断,因此查询用到了name索引,从key_len=74也能看出,age索引列用 在排序过程中(name已经是常量了),因为Extra字段里没有using filesort EXPLAIN select * from employees where name=‘baoliewuqiu’ ORDER BY position 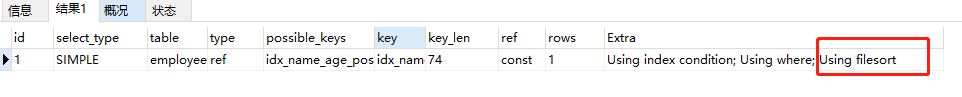 从explain的执行结果来看:key_len=74,查询使用了name索引,由于用了position进行排序,跳过了 age,出现了Using filesort。 从explain的执行结果来看:key_len=74,查询使用了name索引,由于用了position进行排序,跳过了 age,出现了Using filesort。 EXPLAIN select * from employees where name=‘bbaoliewuqiu’ ORDER BY age,position 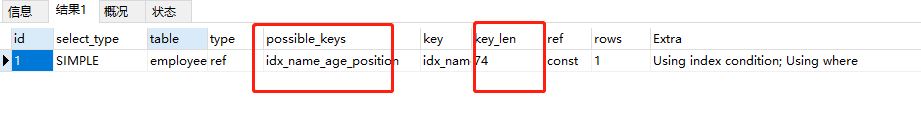 查找只用到索引name,age和position用于排序,无Using filesort。 查找只用到索引name,age和position用于排序,无Using filesort。 EXPLAIN select * from employees where name=‘baoliewuqiu’ ORDER BY position,age 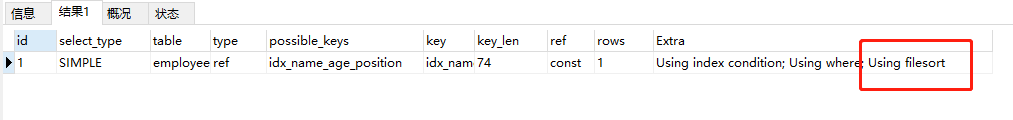 和Case 3中explain的执行结果一样,但是出现了Using filesort,因为索引的创建顺序为 name,age,position,但是排序的时候age和position颠倒位置了。 和Case 3中explain的执行结果一样,但是出现了Using filesort,因为索引的创建顺序为 name,age,position,但是排序的时候age和position颠倒位置了。 EXPLAIN select * from employees where name=‘baoliewuqiu’ and age=18 ORDER BY position,age  与Case 4对比,在Extra中并未出现Using filesort,因为age为常量,在排序中被优化(相当于order by age没有起作用),所以索引未颠倒, 不会出现Using filesort。 与Case 4对比,在Extra中并未出现Using filesort,因为age为常量,在排序中被优化(相当于order by age没有起作用),所以索引未颠倒, 不会出现Using filesort。 EXPLAIN select * from employees where name=‘baoliewuqiu’ ORDER BY age,position desc 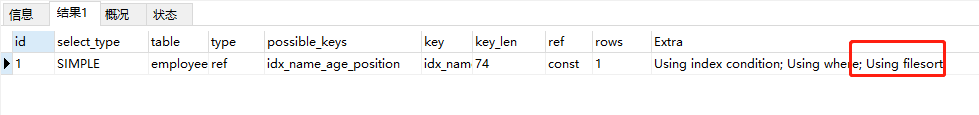 虽然排序的字段列与索引顺序一样,且order by默认升序,这里position desc变成了降序,导致与索引的排序方式不同,从而产生Using filesort。Mysql8以上版本有降序索引可以支持该种查询方式。 虽然排序的字段列与索引顺序一样,且order by默认升序,这里position desc变成了降序,导致与索引的排序方式不同,从而产生Using filesort。Mysql8以上版本有降序索引可以支持该种查询方式。 EXPLAIN select * from employees where name in (‘baoliewuqiu’,‘feifei’) ORDER BY age,position  对于排序来说,多个相等条件也是范围查询 对于排序来说,多个相等条件也是范围查询
优化总结
MySQL支持两种方式的排序filesort和index,Using index是指MySQL扫描索引本身完成排序。index 效率高,filesort效率低。order by满足两种情况会使用Using index。 2.1) order by语句使用索引最左前列。 2.2) 使用where子句与order by子句条件列组合满足索引最左前列。尽量在索引列上完成排序,遵循**索引建立(索引创建的顺序)**时的最左前缀法则。如果order by的条件不在索引列上,就会产生Using filesort。能用覆盖索引尽量用覆盖索引group by与order by很类似,其实质是先排序后分组,遵照索引创建顺序的最左前缀法则。对于group by的优化如果不需要排序的可以加上order by null禁止排序。注意,where高于having,能写在where中 的限定条件就不要去having限定了。
6.Using filesort文件排序
当然,能尽然使用索引排序用索引排序,但是工作中某些特别骚的sql就是用到了文件排序,那我们也要了解了解,能优化就优化,不能优化,缓存redis或者搜索硬引擎elasticserch~~233333
filesort文件排序方式
单路排序:是一次性取出满足条件行的所有字段,然后在sort buffer中进行排序;用trace工具可 以看到sort_mode信息里显示< sort_key, additional_fields >或者< sort_key, packed_additional_fields >双路排序(又叫回表排序模式):是首先根据相应的条件取出相应的排序字段和可以直接定位行 数据的行 ID,然后在 sort buffer 中进行排序,排序完后需要再次取回其它需要的字段;用trace工具 可以看到sort_mode信息里显示< sort_key, rowid >
MySQL 通过比较系统变量 max_length_for_sort_data(默认1024字节) 的大小和需要查询的字段总大小来 判断使用哪种排序模式。
如果 max_length_for_sort_data 比查询字段的总长度大,那么使用 单路排序模式;如果 max_length_for_sort_data 比查询字段的总长度小,那么使用 双路排序模式;
下面我们来看下这条sql语句 EXPLAIN select * from employees where name=‘lilei’ ORDER BY position 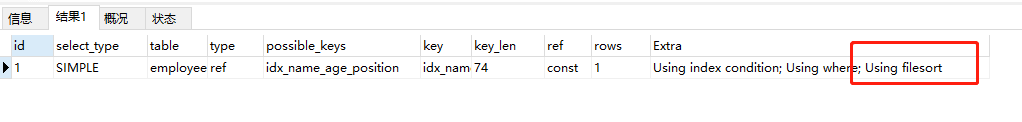 我们用trace分析一下(因为trace结果太多,博主只粘贴了显示排序的部分) 我们用trace分析一下(因为trace结果太多,博主只粘贴了显示排序的部分)
select * from employees where name='lilei' ORDER BY position ;
SELECT * FROM information_schema.OPTIMIZER_TRACE;
{
"steps": [
{
"join_execution": { ‐‐Sql执行阶段
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
{
"filesort_information": [
{
"direction": "asc",
"table": "`employees`",
"field": "position"
}
] /* filesort_information */,
"filesort_priority_queue_optimization": {
"usable": false,
"cause": "not applicable (no LIMIT)"
} /* filesort_priority_queue_optimization */,
"filesort_execution": [
] /* filesort_execution */,
"filesort_summary": { ‐‐文件排序信息
"rows": 1, ‐‐预计扫描行数
"examined_rows": 1, ‐‐参数排序的行
"number_of_tmp_files": 0, ‐‐使用临时文件的个数,这个值如果为0代表全部使用的sort_buffer内存排序,否则使用的 磁盘文件排序
"sort_buffer_size": 200704, ‐‐排序缓存的大小
"sort_mode": "" ‐‐排序方式,这里用的单路排序
} /* filesort_summary */
}
] /* steps */
} /* join_execution */
}
] /* steps */
}
因为博主这里的数据量比较少,就三行数据。各位看官可以
表中多插入几万数据根据name查询出来的结果多一点.set max_length_for_sort_data = 10; (employees表所有字段长度总和肯定大于10字节)设置小一点。
再执行之前的sql,用trace工具看一下,就会发现变成了双路排序,博主就不贴图了这里。
单路排序的详细过程:
从索引name找到第一个满足 name = ‘xx’ 条件的主键 id根据主键 id 取出整行,取出所有字段的值,存入 sort_buffer 中从索引name找到下一个满足 name = ‘xx’ 条件的主键 id.重复步骤 2、3 直到不满足 name = ‘xx’对 sort_buffer 中的数据按照字段 position 进行排序返回结果给客户端
双路排序的详细过程:
从索引 name 找到第一个满足 name = ‘xx’ 的主键id根据主键 id 取出整行,把排序字段 position 和主键 id 这两个字段放到 sort buffer 中从索引 name 取下一个满足 name = ‘xx’ 记录的主键 id重复 3、4 直到不满足 name = ‘xx’对 sort_buffer 中的字段 position 和主键 id 按照字段 position 进行排序遍历排序好的 id 和字段 position,按照 id 的值回到原表中取出 所有字段的值返回给客户端
对比两个排序模式,单路排序会把所有需要查询的字段都放到 sort buffer 中,而双路排序只会把主键和需要排序的字段放到 sort buffer 中进行排序,然后再通过主键回到原表查询需要的字段。
如果 MySQL 排序内存配置的比较小并且没有条件继续增加了,可以适当把 max_length_for_sort_data 配 置小点,让优化器选择使用双路排序算法,可以在sort_buffer 中一次排序更多的行,只是需要再根据主键 回到原表取数据。如果 MySQL 排序内存有条件可以配置比较大,可以适当增大 max_length_for_sort_data 的值,让优化器 优先选择全字段排序(单路排序),把需要的字段放到 sort_buffer 中,这样排序后就会直接从内存里返回查 询结果了。
所以,MySQL通过 max_length_for_sort_data 这个参数来控制排序,在不同场景使用不同的排序模式, 从而提升排序效率。 注意,如果全部使用sort_buffer内存排序一般情况下效率会高于磁盘文件排序,但不能因为这个就随便增 大sort_buffer(默认1M),mysql很多参数设置都是做过优化的,不要轻易调整。
7.结语
世上无难事,只怕有心人,每天积累一点点,fighting!!!
|
 这里没有走索引,分析如下: 如果用name索引需要遍历name字段联合索引树,然后还需要根据遍历出来的主键值去主键索引树里再去查出最终数据,成本比全表扫描 还高。(name是非主键索引,也称辅助索引,其叶子节点存储的是主键id。所以会查两次) 可以用覆盖索引优化,这样只需要遍历name字段的联合索引树就能拿到所有结果(因以为要查询的数据都在联合索引里面,所以只要查一次索引树,成本会比全表扫描还高),如下:
这里没有走索引,分析如下: 如果用name索引需要遍历name字段联合索引树,然后还需要根据遍历出来的主键值去主键索引树里再去查出最终数据,成本比全表扫描 还高。(name是非主键索引,也称辅助索引,其叶子节点存储的是主键id。所以会查两次) 可以用覆盖索引优化,这样只需要遍历name字段的联合索引树就能拿到所有结果(因以为要查询的数据都在联合索引里面,所以只要查一次索引树,成本会比全表扫描还高),如下: 那么,神奇的地方来了,我们再来看看这条sql
那么,神奇的地方来了,我们再来看看这条sql 可能有小伙伴就会蒙蔽了,为何这句就走索引了,这和刚才 name > ‘a’ 不是差不么? 分析:
可能有小伙伴就会蒙蔽了,为何这句就走索引了,这和刚才 name > ‘a’ 不是差不么? 分析: 因为是以json格式输出的,将这一栏数据copy出来,去json转换的网站格式化看一下,请认真看下博主加注释的地方,如下:
因为是以json格式输出的,将这一栏数据copy出来,去json转换的网站格式化看一下,请认真看下博主加注释的地方,如下: 利用最左前缀法则:中间字段不能断,因此查询用到了name索引,从key_len=74也能看出,age索引列用 在排序过程中(name已经是常量了),因为Extra字段里没有using filesort
利用最左前缀法则:中间字段不能断,因此查询用到了name索引,从key_len=74也能看出,age索引列用 在排序过程中(name已经是常量了),因为Extra字段里没有using filesort 从explain的执行结果来看:key_len=74,查询使用了name索引,由于用了position进行排序,跳过了 age,出现了Using filesort。
从explain的执行结果来看:key_len=74,查询使用了name索引,由于用了position进行排序,跳过了 age,出现了Using filesort。 查找只用到索引name,age和position用于排序,无Using filesort。
查找只用到索引name,age和position用于排序,无Using filesort。 和Case 3中explain的执行结果一样,但是出现了Using filesort,因为索引的创建顺序为 name,age,position,但是排序的时候age和position颠倒位置了。
和Case 3中explain的执行结果一样,但是出现了Using filesort,因为索引的创建顺序为 name,age,position,但是排序的时候age和position颠倒位置了。 与Case 4对比,在Extra中并未出现Using filesort,因为age为常量,在排序中被优化(相当于order by age没有起作用),所以索引未颠倒, 不会出现Using filesort。
与Case 4对比,在Extra中并未出现Using filesort,因为age为常量,在排序中被优化(相当于order by age没有起作用),所以索引未颠倒, 不会出现Using filesort。 虽然排序的字段列与索引顺序一样,且order by默认升序,这里position desc变成了降序,导致与索引的排序方式不同,从而产生Using filesort。Mysql8以上版本有降序索引可以支持该种查询方式。
虽然排序的字段列与索引顺序一样,且order by默认升序,这里position desc变成了降序,导致与索引的排序方式不同,从而产生Using filesort。Mysql8以上版本有降序索引可以支持该种查询方式。 对于排序来说,多个相等条件也是范围查询
对于排序来说,多个相等条件也是范围查询 我们用trace分析一下(因为trace结果太多,博主只粘贴了显示排序的部分)
我们用trace分析一下(因为trace结果太多,博主只粘贴了显示排序的部分)